
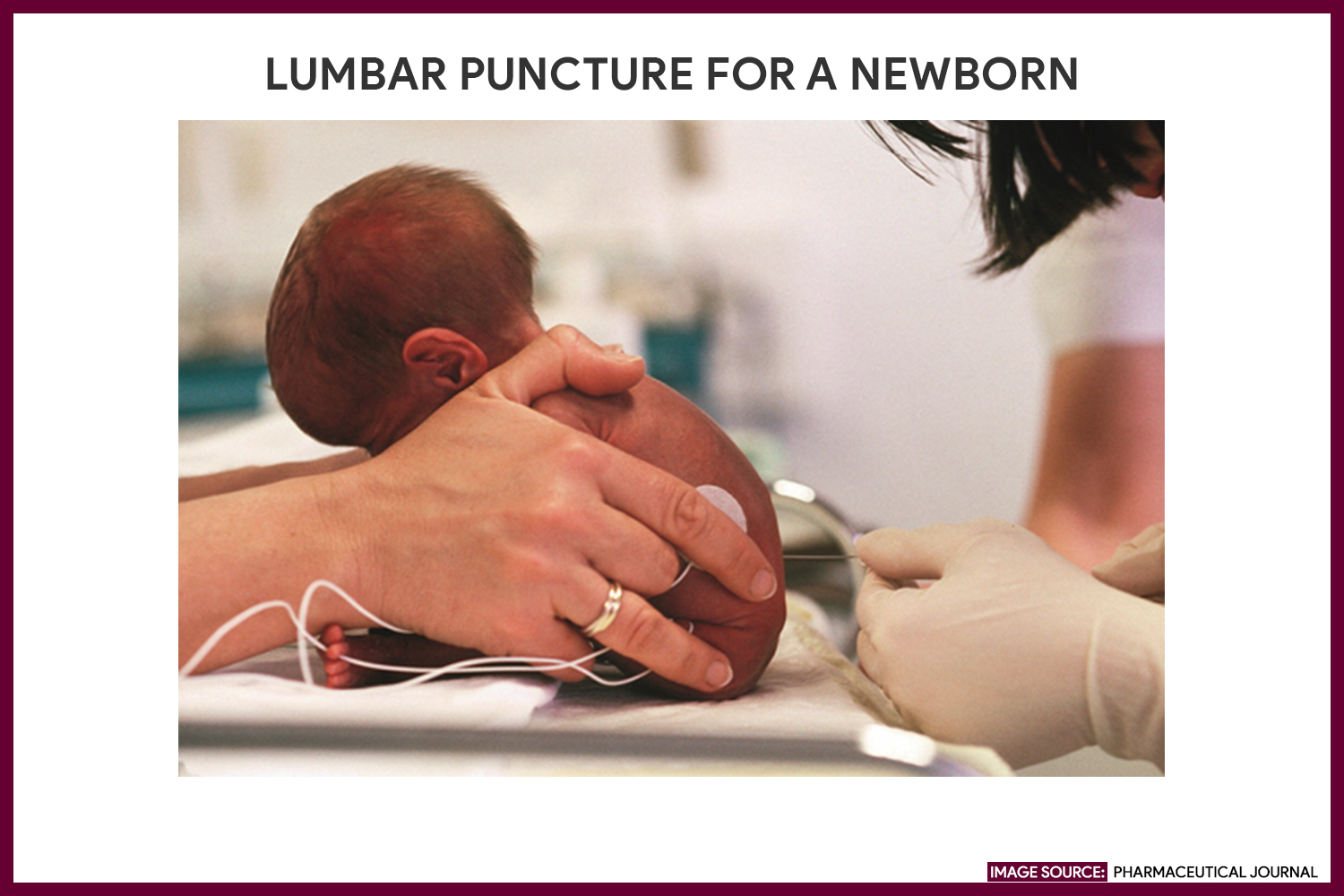
Variations in opening pressure cannot be explained by variations in HH above the needle hub. Figure: Place the patient in a lateral recumbent position, with her knees flexed toward her abdomen, her chin flexed onto her chest, and her back at the. There may be a dressing or a plaster covering the spot where the needle went in. What happens after a lumbar puncture If the lumbar puncture is done to look for infection, the results will usually be available within a few hours. Average head height (HH) above the needle hub (SUFS only) was 28.5 cm (SD 7.9), and no correlation between HH and OP was found (R^2 = 0.06)Ĭonclusion: In the general ED population, opening pressure on patients in the SUFS position is significantly higher than opening pressure in the LD position, with a similar distribution. If opening pressure is needed, the patient needs to be in the lateral decubitus position. A lumbar puncture is done below where the spinal cord ends, so it is not possible to injure the spinal cord. It enables drainage or collection of cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF ) as well as administration of intrathecal medications. The average OP was 14.8 cm higher in the SUFS position (19.8 cm LD vs 34.6 cm SUFS p (SD) of OP pressures were similar (5.7 LD vs 5.9 SUFS) in the two groups. A lumbar puncture is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure in which a spinal needle is passed into the subarachnoid space. There were more women in the LD groups (63% vs. There was no difference in age, height, or discharge rate in either group. Results: Forty-two patients were included in the study (20 SUFS and 22 LD). In SUFS patient, head height above needle hub (measured vertically to the level of the external auditory meatus) was obtained. Physicians performed LP in either the lateral decubitus (LD) or SUFS position, as per clinical judgment. Exclusion criteria were < 18 years old, positive CSF findings, contraindication to LP, known hydrocephalus, structural intracranial abnormality, or ventricular shunt.
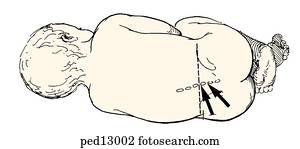
Methods: IRB-approved, prospective study of patients undergoing LP in two urban emergency departments (EDs). When the back is in a curved position, a needle is placed between the bones of the spine (vertebrae) below the level of the spinal cord. Objectives: We sought to identify a range of normal CSF OP in the sitting-up, feet supported position (SUFS), and to determine whether head height above the needle affects the variance of the obtained pressures. There are no data describing the normal range of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) opening pressures (OP) inpatients in the sitting position. For mechanical reasons, practicingphysicians may elect to perform the procedure with the patient in a sitting position. The patient, with a pillow under the head, should curl into a fetal position, placing the lumbar spine in maximal flexion.

Background: Traditionally lumbar puncture (LP) is performed in the lateral decubitus position.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
